1.Rolling performance test
Purpose: To test the rolling performance of caster wheel after loading;
Test equipment: caster single wheel rolling, steering performance testing machine;
Test Methods: As shown in Figure 1, install the caster or wheel on the testing machine, apply the rated load W on the caster along the plumb direction and apply force on the wheel axle in the horizontal direction. Measure the minimum force F1 required to rotate the caster or wheel <at least one-half turn>, F1 being the resistance to rotation of the caster or wheel.
The rolling resistance of a single wheel is calculated according to equation (1).
pl=F1/W…… (1)
Where μ1 rolling resistance coefficient;
F1 rolling resistance, the unit is Niu (N).
W rated load, in Nm (N).
That is: propulsion F1 = load W × resistance coefficient μ1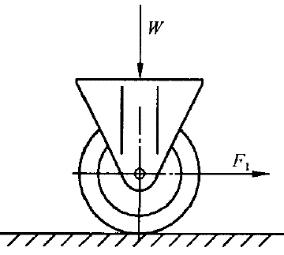
The rolling performance of single wheel of caster shall conform to the national standard GB/T14687-2011 (Table 1).
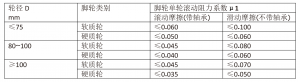
2.Steering performance test
Purpose: To test the steering performance of universal casters after loading;
Test equipment: caster rotation steering performance test machine.
Test Method: As shown in Fig. 2, install the caster or wheel on the testing machine, apply the rated load W to the caster along the plumb direction, and apply the force in the horizontal direction perpendicular to the forward direction of the wheel. Measure the minimum force F2 to steer the caster, F2 is the steering resistance of the caster. The coefficient of steering resistance is calculated according to equation (1).
μ2=F2/W …… (1)
where μ2 is the coefficient of steering resistance.
F2 Steering resistance, in Nm; W Rated load, in Nm.
W rated load in Nm.
i.e.: pushing force F2=load wX resistance coefficient μ2
The steering performance shall comply with the national standard GB/T14687-2011 (Table 2). 
3. Description of test values.
The resistance coefficient of the test from 1, from 2 the smaller, indicating that the smaller the resistance, the easier to use, better flexibility: on the contrary, the larger the value, the greater the resistance, the more laborious to use.
4. The relationship between caster wheel surface material, movable frame disc material, ball material and resistance.
1) The harder the hardness of caster wheel surface (such as PA, MC, PP, iron wheel, etc.), the smaller the resistance coefficient, the easier it is to push, but the worse it is for the protection effect of the ground and the mute effect.
2) When the surface of caster wheel is soft material (such as TPU, TPR, BR, etc.), the greater the resistance coefficient, the greater the driving force required, but the better the effect of ground protection and mute effect.
3) The higher the hardness of the movable wheel bracket disc and ball material, the lower the steering resistance coefficient and the easier it is to push.
Post time: Apr-24-2024