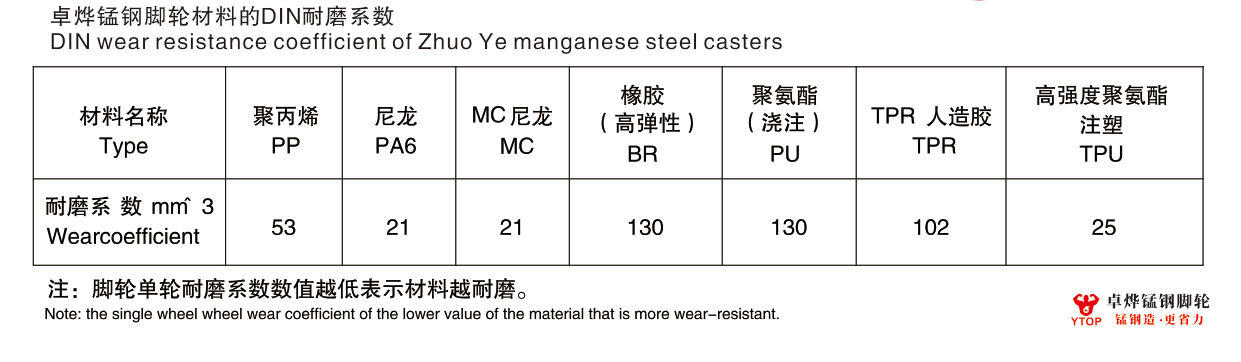
In industrial applications, the wear resistance of caster materials is one of the key indicators for assessing their quality and suitability. For this reason, DIN wear tests are widely used to quantitatively assess the abrasion performance of caster materials under specific conditions. The aim of this paper is to present the purpose, principle, procedure and result analysis of DIN wear testing of single wheel materials.
I. Test purpose
DIN wear test is designed to simulate the wear process of caster materials in actual application, and evaluate the surface wear condition, weight loss, volume loss and wear thickness of the test material through friction at a certain length distance. By comparing with the standard rubber, the wear resistance of the material can be evaluated more intuitively, providing a scientific basis for product design and material selection.
Testing Principle
DIN abrasion test is carried out by roller type friction and wear tester. At a specified contact pressure and a given area, the specimen is pressed firmly against a drum with sandpaper and moved laterally along the drum. This movement causes abrasion to occur at one end of the cylindrical specimen. By measuring the change in the mass of the specimen before and after the test and combining it with the density of the specimen, the volumetric abrasion can be calculated.
Test Flow
1. Specimen preparation: Cut three representative specimens using a drill cutter to ensure that the size and shape of the specimens meet the test requirements.
2. Pre-test mass measurement: The mass of each specimen prior to testing is accurately measured using an electronic hydrometer and the data recorded.
3. Test Setup: Apply the sandpaper pack to the surface of the drum and adjust the test equipment to ensure that the contact pressure and area of the specimen with the drum meets the test requirements.
4. Starting the test: The specimen is placed on the drum and the test equipment is activated. During the test, the specimen moves laterally along the drum, creating abrasion. If the specimen is unable to complete the full test, the option of testing half way is available.
5. Post-test mass measurement: When the specimen has completed the full (or second half) of the test, its mass is again measured using an electronic hydrometer and the data recorded.
IV. Analysis of results
Based on the mass data before and after the test, the mass loss of the specimen can be calculated. Combined with the density of the specimen, the volumetric wear is further calculated. Comparing the test results with the standard rubber, the abrasion resistance of the caster material can be evaluated. If the mass loss and volumetric abrasion of the specimen are small, it means that the abrasion resistance is good; on the contrary, the abrasion resistance is poor.
In addition, it can also be combined with the surface wear condition of the specimen for comprehensive analysis. For example, observe whether the surface of the specimen shows obvious scratches, abrasion or flaking, etc., to further assess the wear resistance of the material.
In conclusion, the DIN wear test for single wheel materials is an effective method to assess the wear resistance of caster materials. Through this test, the wear resistance characteristics of the material can be quantitatively assessed, providing a scientific basis for product design and material selection.
Post time: Nov-21-2024